CRM Software for Small Business Success
CRM Software for Small Business: Navigating the complexities of customer relationships is crucial for any small business aiming for sustainable growth. Effective CRM software offers a streamlined solution, consolidating customer interactions, automating tasks, and ultimately boosting efficiency and profitability. This exploration delves into the essential features, implementation strategies, and ROI considerations for small businesses seeking to leverage the power of CRM.
From selecting the right software to integrating it seamlessly with existing business tools, we’ll cover the key aspects to help you make informed decisions and optimize your customer management processes. Understanding the unique needs of small businesses, this guide provides practical advice and actionable insights to help you harness the full potential of CRM technology.
Defining Needs for Small Business CRM
Implementing a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system can significantly benefit small businesses by streamlining operations and fostering growth. Many small businesses initially operate without a CRM, often relying on spreadsheets or email chains to manage customer interactions. This approach, however, quickly becomes unsustainable as the business expands.
Key Challenges Faced by Small Businesses Without CRM Software
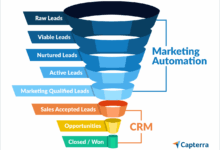
Small businesses without a dedicated CRM system often struggle with three primary challenges: disorganized customer data, inefficient communication, and difficulty tracking sales progress. These issues directly impact productivity, customer satisfaction, and ultimately, profitability. Addressing these challenges effectively requires a well-structured CRM solution tailored to the specific needs of the small business.
Essential Features of a Small Business CRM
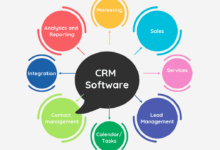
To overcome the aforementioned challenges, a small business CRM should include core functionalities such as contact management, communication tools, and sales pipeline tracking. Contact management features should allow for easy storage and retrieval of customer information, including contact details, purchase history, and interaction logs. Effective communication tools, including email integration and potentially SMS capabilities, ensure timely and personalized interactions with customers. Finally, sales pipeline tracking helps visualize the sales process, identify bottlenecks, and predict future revenue. These features work synergistically to provide a holistic view of customer relationships and sales performance.
Comparison of Small Business and Enterprise CRM Needs
While both small businesses and large enterprises benefit from CRM systems, their needs differ significantly in scale and complexity. Small businesses typically require simpler, more user-friendly systems with a focus on core functionalities. They often prioritize ease of use and affordability over highly advanced features. In contrast, large enterprises need sophisticated CRM solutions capable of handling vast amounts of data, integrating with numerous other systems, and supporting complex workflows and reporting. Their requirements extend to advanced analytics, automation, and customization options, which are often unnecessary and cost-prohibitive for smaller organizations. Essentially, small businesses need a focused, efficient system, whereas large enterprises need a scalable and highly adaptable platform.
Comparison of CRM Pricing Models for Small Businesses
| Pricing Model | Monthly Cost (Estimate) | Feature Limitations | Customer Support Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Freemium | $0 – $20 | Limited number of users, contacts, and features; often includes branding from the provider. | Basic email or community forum support. |
| Subscription (Basic) | $20 – $50 | More users and features than freemium, but may still have limitations on advanced analytics or integrations. | Phone and email support, potentially with access to knowledge bases and online tutorials. |
| One-Time Purchase | Varies greatly, often a higher upfront cost | Features are typically fixed at the time of purchase; may lack ongoing updates and support. | Limited support, often only covering initial setup and troubleshooting. |
Exploring CRM Software Options for Small Businesses
Choosing the right CRM software can significantly improve a small business’s efficiency and customer relationships. This section explores various CRM options, their applications, and implementation considerations for small businesses.
Popular CRM Software Options for Small Businesses
Several CRM platforms cater specifically to the needs and budgets of small businesses. Selecting the right one depends on factors such as the size of your customer base, the complexity of your sales process, and your budget.
- HubSpot CRM: A free and user-friendly option, HubSpot CRM is ideal for small businesses starting out. Key features include contact management, deal tracking, and basic email marketing tools. Its target user profile is businesses with limited budgets and simpler sales processes needing basic CRM functionalities.
- Zoho CRM: A more comprehensive and scalable solution than HubSpot, Zoho CRM offers a wider range of features, including sales automation, customer support tools, and integration with other Zoho applications. It’s suitable for businesses with growing customer bases and more complex sales processes.
- Salesforce Essentials: A simplified version of the powerful Salesforce platform, Salesforce Essentials is designed for small businesses. It offers robust contact management, sales pipeline management, and reporting capabilities. It targets businesses needing a powerful yet accessible CRM solution with potential for future scalability.
- Freshsales: This CRM prioritizes sales automation and team collaboration. Key features include automated workflows, sales forecasting, and mobile accessibility. It is well-suited for sales-driven businesses needing efficient sales processes and team coordination.
- Pipedrive: Pipedrive focuses on sales pipeline visualization and management. Its intuitive interface makes it easy to track deals and manage sales activities. It’s a good choice for businesses that prioritize sales pipeline visibility and efficiency.
CRM Software Utilization Across Different Small Businesses
Different business types will leverage CRM software in unique ways.
- Bakery: A bakery might use a CRM to manage customer orders, track loyalty program participation, and send targeted promotions based on past purchases. For example, they could track customer preferences for specific pastries and send personalized birthday offers or promotions for seasonal items.
- Consulting Firm: A consulting firm would utilize a CRM to manage client projects, track billable hours, and maintain client communication records. This ensures consistent project tracking, accurate invoicing, and facilitates seamless client interaction across the team.
- Retail Store: A retail store could use a CRM to manage inventory, track customer purchases, and personalize marketing campaigns based on customer segmentation. For example, they could segment customers by purchase history and send targeted email campaigns for new product launches or sales events.
Cloud-Based versus On-Premise CRM Solutions
The choice between cloud-based and on-premise CRM solutions involves several considerations.
- Cloud-Based CRM: Offers accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection, automatic updates, and typically lower upfront costs. However, it relies on a stable internet connection and data security depends on the provider’s infrastructure.
- On-Premise CRM: Provides greater control over data security and customization options. However, it requires significant upfront investment in hardware and software, ongoing maintenance, and IT expertise for installation and management.
Implementing a New CRM System in a Small Business
Implementing a new CRM system requires a structured approach.
- Define Requirements: Clearly identify your business needs and objectives for the CRM.
- Select a CRM Solution: Choose a CRM that aligns with your budget, technical capabilities, and business requirements.
- Data Migration: Transfer existing customer data into the new CRM system accurately and efficiently.
- User Training: Provide comprehensive training to employees on how to use the new CRM system effectively.
- System Integration: Integrate the CRM with other business systems, such as accounting and marketing automation tools.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Optimization: Regularly monitor system performance and make adjustments as needed to optimize its effectiveness.
Data Management and Integration with CRM
Effective data management is the cornerstone of a successful small business. A well-implemented CRM system significantly enhances this process, providing a centralized hub for all customer-related information and streamlining interactions. This section explores the crucial role of data security and privacy within a CRM, demonstrates how organized data improves customer relationships, and illustrates the benefits of integrating your CRM with other essential business tools.
Data Security and Privacy in Small Business CRM
Protecting sensitive customer data is paramount. A robust CRM system should incorporate multiple security measures, including data encryption both in transit and at rest, access controls based on user roles and permissions, and regular security audits. Compliance with relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) or CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), is crucial. Failing to protect customer data can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. Investing in a CRM with strong security features is not just a good practice; it’s a necessity.
CRM Software and Improved Customer Relationship Management
CRM software organizes customer data—contact details, purchase history, communication logs, and support interactions—into a single, easily accessible database. This consolidated view eliminates data silos and provides a comprehensive understanding of each customer. Sales teams gain insights into customer preferences and buying patterns, leading to more effective sales strategies and personalized customer experiences. Marketing teams can segment customers for targeted campaigns, improving campaign effectiveness and ROI. Customer service teams can quickly access customer history to resolve issues efficiently, enhancing customer satisfaction. This improved data organization translates directly into stronger customer relationships and increased loyalty.
Integration of CRM Systems with Other Business Tools
The true power of a CRM system is unlocked through integration with other business tools. Seamless data flow between different platforms eliminates manual data entry, reduces errors, and improves overall efficiency. For example, integrating your CRM with an email marketing platform allows for automated email sequences based on customer actions or lifecycle stages. Integration with accounting software automates invoicing and payment processing, improving financial management. Similarly, integration with social media platforms provides valuable customer insights and allows for direct engagement. This interconnected approach creates a holistic view of your business operations and empowers your teams to work more effectively.
CRM Software Integration Capabilities
The following table compares the integration capabilities of three popular CRM systems—HubSpot, Salesforce, and Zoho CRM—with common small business tools. Note that specific integration options may vary depending on the chosen plan and version.
| CRM Software | Email Marketing | Accounting Software | E-commerce Platforms |
|---|---|---|---|
| HubSpot | Native Integration | Integrates with Xero, QuickBooks | Integrates with Shopify, Magento |
| Salesforce | Integrates with Mailchimp, Constant Contact | Integrates with NetSuite, QuickBooks | Integrates with various platforms via AppExchange |
| Zoho CRM | Native Integration | Integrates with Zoho Books, Xero, QuickBooks | Integrates with Shopify, Magento |
Measuring ROI and Assessing Success
Implementing a CRM system represents a significant investment for any small business. Therefore, understanding its return on investment (ROI) is crucial for justifying the expense and ensuring continued success. This section outlines key metrics for measuring ROI, demonstrates how CRM contributes to business growth, and provides guidance on visualizing the impact of CRM over time.
Key Metrics for Measuring CRM ROI
Three key metrics effectively measure the return on investment of CRM software for small businesses: increased sales revenue, improved customer satisfaction, and reduced operational costs. Tracking these metrics provides a comprehensive understanding of the CRM’s overall impact.
CRM’s Contribution to Business Growth
CRM software directly contributes to increased sales by streamlining sales processes, improving lead management, and facilitating more effective sales team collaboration. Sales representatives gain a centralized view of customer interactions, allowing them to personalize outreach and close deals more efficiently. Furthermore, CRM systems enhance customer satisfaction through improved communication, personalized service, and proactive issue resolution. By tracking customer interactions and preferences, businesses can anticipate needs and deliver a more tailored experience, fostering loyalty and repeat business. Finally, CRM software reduces operational costs by automating repetitive tasks, such as data entry and reporting, freeing up employee time for more strategic initiatives. Improved efficiency in lead nurturing, customer support, and sales processes minimizes wasted resources and contributes to significant cost savings.
Visualizing CRM Impact: A Six-Month Analysis
To illustrate the impact of CRM software on key business metrics, a visual representation is highly beneficial. This allows for easy understanding and clear communication of results.
A simple bar chart comparing key metrics (sales revenue, customer satisfaction scores, and operational costs) before and after CRM implementation can effectively demonstrate the changes. Each bar would represent a two-month period, showing the trend over six months.
Alternatively, a line graph could track the same metrics over the six-month period, illustrating the trajectory of improvement. This provides a more dynamic view of the CRM’s ongoing influence.
For customer satisfaction, a combination chart could display both the average customer satisfaction score and the number of customer support tickets resolved. This would visually demonstrate the correlation between improved satisfaction and reduced support workload.
For example, let’s consider a hypothetical small business, “Acme Widgets,” that implemented a CRM system six months ago. Assume that before implementation, their average monthly sales were $10,000, customer satisfaction score was 70%, and operational costs related to customer service were $2,000. After six months of using the CRM, their average monthly sales increased to $15,000, their customer satisfaction score rose to 85%, and operational costs decreased to $1,500. This data can be effectively visualized using a bar chart showing the before and after values for each metric. A line graph could further illustrate the month-by-month improvement over the six-month period. For instance, the line graph for sales revenue would show a steady increase from $10,000 to $15,000 over the six months, clearly demonstrating the positive impact of the CRM. Similarly, the line graph for operational costs would display a downward trend, showing the cost savings achieved through increased efficiency. The combination chart for customer satisfaction would showcase both the rising satisfaction score and the decreasing number of support tickets, illustrating the positive correlation between these two metrics. These visual representations provide a compelling narrative of the CRM’s success in boosting sales, improving customer satisfaction, and reducing operational costs.
End of Discussion
Implementing the right CRM software can significantly transform a small business, fostering stronger customer relationships, streamlining operations, and driving revenue growth. By carefully considering your specific needs, selecting the appropriate features, and monitoring key performance indicators, you can unlock the full potential of CRM and achieve lasting success. Remember, a well-integrated CRM system isn’t just about managing data; it’s about building lasting relationships that fuel your business’s growth.