CRM for Sales and Marketing Automation
CRM for Sales and Marketing Automation represents a powerful synergy, streamlining processes and boosting efficiency for businesses of all sizes. This integration moves beyond simply managing customer relationships; it fosters a holistic approach where sales and marketing teams work in perfect harmony, leveraging data-driven insights to optimize campaigns and nurture leads more effectively. The result? Increased revenue, improved customer satisfaction, and a significant return on investment.
This exploration delves into the core functionalities of such a system, highlighting key differences between standalone CRM solutions and those integrated with marketing automation. We will examine the benefits of this integration, showcasing real-world case studies and exploring the impact on lead nurturing and conversion rates. Furthermore, we will provide a practical guide to implementation, management, and the selection of the right CRM solution tailored to your specific business needs and future growth.
Defining CRM for Sales and Marketing Automation
A Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system, when enhanced with marketing automation capabilities, becomes a powerful tool for streamlining business processes and boosting revenue. It centralizes customer data, automates repetitive tasks, and provides valuable insights for both sales and marketing teams, fostering a more coordinated and effective approach to customer engagement.
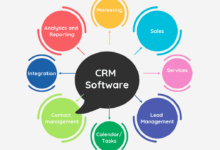
A CRM system designed for both sales and marketing manages all interactions with current and potential customers. Core functionalities include contact management (organizing and tracking customer information), lead management (identifying and qualifying potential customers), sales pipeline management (visualizing the sales process), marketing campaign management (planning, executing, and analyzing marketing efforts), reporting and analytics (measuring key performance indicators), and customer service support (managing customer inquiries and resolving issues). Integration with other business systems, such as email marketing platforms and social media tools, further enhances its capabilities.
Core Differences Between Sales-Only and Integrated CRM Systems
A CRM solely focused on sales primarily tracks leads, manages opportunities, and supports the sales process from initial contact to closing the deal. Conversely, a CRM integrated with marketing automation adds functionalities for creating and managing marketing campaigns, automating email sequences, personalizing customer communications, lead scoring (ranking leads based on their likelihood to convert), and analyzing marketing ROI. The key difference lies in the breadth of functionality; a sales-only CRM is transaction-focused, while an integrated CRM encompasses the entire customer journey, from initial awareness to post-purchase engagement.
Examples of Unified CRM Usage by Sales and Marketing Teams
Imagine a company using a unified CRM. The marketing team can segment customers based on demographics and buying behavior, then launch targeted email campaigns promoting relevant products. The CRM automatically tracks email opens and clicks, feeding this data back into the system to further refine targeting. Sales representatives can access this customer engagement data, understanding individual customer preferences before making contact. This allows for more personalized sales pitches and improved conversion rates. Additionally, when a lead converts into a customer, all interactions are recorded in the CRM, providing a complete history for both sales and marketing teams to use for future engagement and analysis.
Feature Comparison: Standalone CRM vs. Integrated CRM
| Feature | Standalone Sales CRM | Integrated Sales & Marketing CRM |
|---|---|---|
| Contact Management | Basic contact information, notes, and activity tracking | Comprehensive contact information, segmentation capabilities, and interaction history across all channels |
| Lead Management | Lead tracking and assignment to sales representatives | Lead scoring, lead nurturing workflows, and automated lead routing based on predefined criteria |
| Marketing Automation | Limited or no marketing automation capabilities | Email marketing, social media integration, campaign management, and A/B testing |
| Reporting and Analytics | Sales pipeline analysis and sales performance metrics | Comprehensive reporting on sales, marketing, and customer engagement metrics, including ROI on marketing campaigns |
Benefits of Integrated Sales and Marketing Automation
Integrating sales and marketing automation creates a powerful synergy, streamlining processes and boosting overall efficiency. This unified approach eliminates data silos, improves communication, and ultimately drives revenue growth. By connecting previously disparate systems, businesses can gain a holistic view of their customer journey, leading to more effective strategies and improved ROI.
Improved Efficiency Through Integrated Systems
An integrated system eliminates the manual data entry and reconciliation that often plagues separate sales and marketing platforms. This automation reduces human error, freeing up valuable time for sales and marketing teams to focus on strategic initiatives rather than administrative tasks. For example, lead information automatically updates across both platforms, ensuring everyone has access to the most current data. Marketing campaigns can be more precisely targeted based on real-time sales insights, and sales teams can access pre-qualified leads ready for engagement, streamlining the sales process significantly. The resulting efficiency translates directly into cost savings and increased productivity.
Case Studies Demonstrating ROI
Several companies have reported substantial ROI from implementing integrated sales and marketing automation. For instance, a mid-sized B2B software company saw a 30% increase in lead conversion rates within six months of integrating their CRM and marketing automation platform. This improvement was attributed to more effective lead nurturing and personalized communication. Another example is a retail company that saw a 20% reduction in customer acquisition costs after implementing a similar system. This was largely due to more targeted marketing campaigns and improved sales team efficiency. These successes demonstrate the tangible financial benefits of such integration.
Impact on Lead Nurturing and Conversion Rates
Integrated systems significantly enhance lead nurturing by providing a holistic view of the customer journey. Marketing automation tools can automatically segment leads based on their behavior and engagement level, allowing for personalized messaging at each stage of the sales funnel. Sales teams can then access this detailed information, enabling them to engage prospects with tailored approaches. This personalized engagement leads to higher levels of engagement and ultimately, improved conversion rates. For example, a series of automated email sequences can nurture leads who haven’t yet converted, keeping them engaged and moving them closer to a purchase. This consistent and personalized communication is key to increasing conversion rates.
Workflow Improvements Visualization
Imagine a flowchart. On the left, we have the disconnected system: Marketing generates leads, sends them to Sales via email or spreadsheet. Sales manually enters data into their CRM, often encountering inconsistencies. The process is slow, prone to errors, and lacks visibility. Now, consider the integrated system on the right: Marketing generates leads, which are automatically transferred to the CRM. Sales has immediate access to detailed lead information. Marketing receives real-time feedback on campaign performance. The entire process is streamlined, automated, and transparent, with clear visibility at each stage. This visual representation highlights the improved efficiency and collaboration resulting from integration. The reduction in manual data entry, improved communication, and streamlined processes contribute to significantly improved workflow efficiency.
Key Features of a CRM for Sales and Marketing Automation
A robust CRM system for sales and marketing automation goes beyond simple contact management. It integrates various tools and functionalities to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and ultimately drive revenue growth. The key features outlined below represent a core set of capabilities that contribute to a successful implementation, offering benefits across sales and marketing teams.
Lead Management Features
Effective lead management is crucial for nurturing prospects and converting them into customers. A successful CRM facilitates this process through several key features. These features help sales and marketing teams track interactions, qualify leads, and prioritize outreach efforts.
- Lead Scoring: This feature automatically assigns scores to leads based on pre-defined criteria (e.g., website activity, email engagement, demographics). Higher-scoring leads are prioritized for sales follow-up. For example, a lead who downloads a pricing guide and attends a webinar might receive a higher score than one who only visited the website.
- Lead Routing: Leads are automatically assigned to the most appropriate sales representative based on factors like territory, industry, or product interest. This ensures efficient lead distribution and reduces response times.
- Lead Nurturing Workflows: Automated email sequences and other communication methods are triggered based on lead behavior and engagement. This helps keep leads engaged and move them through the sales funnel. For example, a series of emails could educate a lead on the product benefits, followed by a personalized call from a sales representative.
- Lead Segmentation: The ability to group leads based on shared characteristics (demographics, firmographics, behavior) allows for targeted marketing campaigns and personalized communication.
Marketing Campaign Management and Tracking
Effective marketing campaign management requires detailed tracking and analysis to optimize performance. A CRM equipped for this offers several functionalities. These features allow marketers to measure ROI, refine strategies, and maximize their marketing budget.
- Campaign Creation and Scheduling: The CRM should allow for easy creation and scheduling of various marketing campaigns, including email marketing, social media campaigns, and more. This often involves integration with other marketing automation platforms.
- Marketing Automation Workflows: Automated email sequences, drip campaigns, and other automated processes are essential for nurturing leads and driving conversions. These workflows are triggered by specific lead actions or time-based schedules.
- A/B Testing: The ability to test different versions of marketing materials (e.g., subject lines, email copy, landing pages) allows marketers to identify what resonates best with their audience. This iterative approach leads to improved campaign performance.
- Comprehensive Reporting and Analytics: Detailed reports and dashboards provide insights into campaign performance, including open rates, click-through rates, conversion rates, and ROI. This data is crucial for making data-driven decisions to improve future campaigns. For instance, analyzing email open rates can reveal the effectiveness of subject lines and call to actions.
Sales Pipeline Visualization and Reporting
Visualizing the sales pipeline and generating reports are crucial for sales management and forecasting. This gives sales managers real-time insights into the sales process, enabling proactive management and improved sales performance.
- Pipeline Visualization: A visual representation of the sales pipeline, showing the stages of the sales process and the number of deals at each stage, allows for easy monitoring of sales progress. This provides a clear picture of the sales funnel’s health and identifies potential bottlenecks.
- Sales Forecasting: The CRM should enable sales forecasting based on historical data and current pipeline activity. This helps businesses plan for future revenue and allocate resources effectively. For example, accurate forecasting allows for better budgeting and resource allocation for sales team expansion or marketing campaigns.
- Sales Reporting and Analytics: Comprehensive sales reports and dashboards provide insights into sales performance, including sales by representative, sales by product, and sales by region. This data helps identify top performers, areas for improvement, and trends in sales activity.
Essential Features for Small Businesses
Small businesses often need a simpler, more cost-effective solution. While the features above are beneficial for all sizes, some are particularly crucial for smaller teams.
- Ease of Use: Intuitive interface and user-friendly design are paramount for small businesses with limited IT resources.
- Contact Management: Robust contact management capabilities are fundamental for keeping track of customer interactions and building relationships.
- Email Marketing Integration: Seamless integration with email marketing platforms is essential for efficient lead nurturing and communication.
- Basic Reporting and Analytics: Access to key metrics like conversion rates and sales revenue is important for tracking progress and making data-driven decisions.
Implementing and Managing a CRM System
Successfully implementing a CRM system requires a strategic approach encompassing planning, execution, and ongoing management. A well-executed implementation ensures the system aligns with business goals and delivers a strong return on investment. Failure to plan effectively can lead to low user adoption, inaccurate data, and ultimately, a failed CRM initiative.
Step-by-Step CRM Implementation Guide
Implementing a new CRM involves a series of well-defined steps. Careful consideration at each stage is critical to a successful outcome. Rushing the process often results in unforeseen problems later.
- Needs Assessment and Planning: Define your business objectives and identify specific CRM requirements. This includes determining which departments will use the system and what functionalities are essential. For example, a sales team might need strong lead management features, while marketing may prioritize campaign tracking and analytics. Thorough planning helps avoid choosing a system with features you don’t need, or lacking features you do.
- CRM Selection and Vendor Evaluation: Research and compare different CRM vendors, considering factors like cost, features, scalability, and integration capabilities. Request demos and thoroughly evaluate each option before making a decision. Consider cloud-based vs. on-premise solutions based on your IT infrastructure and security needs.
- Data Migration and Cleansing: Migrate existing customer and prospect data into the new CRM system. This is a crucial step that requires careful planning and execution to avoid data loss or corruption. Before migration, cleanse and standardize your data to ensure accuracy and consistency. This may involve removing duplicates, correcting inconsistencies, and enriching data with additional information.
- System Configuration and Customization: Configure the CRM system to match your specific business processes and workflows. This may involve customizing fields, creating workflows, and integrating with other business tools. Proper configuration ensures the system fits your needs and isn’t cumbersome to use.
- Testing and User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Conduct thorough testing to identify and resolve any bugs or issues before the full rollout. Involve key users in User Acceptance Testing to ensure the system meets their needs and is user-friendly. This step is essential to avoid costly post-launch fixes and user frustration.
- Deployment and Go-Live: Deploy the CRM system to your users. A phased rollout can be beneficial, allowing you to address any issues in a controlled manner. Provide comprehensive documentation and support to your users during the initial deployment phase.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Optimization: Continuously monitor the CRM system’s performance and make adjustments as needed. Regularly review key metrics and user feedback to identify areas for improvement. This ensures the CRM remains a valuable tool for your business.
User Training and Adoption Strategies
Effective user training and ongoing support are crucial for maximizing CRM adoption. Without proper training, users may struggle to utilize the system effectively, leading to low adoption rates and ultimately, a poor return on investment.
A multi-faceted approach to training is recommended. This includes:
- Comprehensive training materials: Provide users with easy-to-understand manuals, tutorials, and videos. These should cover all essential aspects of the CRM system, including data entry, reporting, and other key functionalities.
- Hands-on training sessions: Conduct interactive training sessions where users can practice using the CRM system in a guided environment. This allows for immediate feedback and clarification of any questions.
- Ongoing support and mentorship: Provide ongoing support and mentorship to users after the initial training. This may involve creating a dedicated help desk or assigning experienced users as mentors to assist new users.
- Gamification and incentives: Consider using gamification and incentives to encourage user engagement and adoption. For example, you could reward users for consistently using the CRM system or for achieving specific goals.
Data Management and Security Best Practices
Maintaining data integrity and ensuring data security are paramount when using a CRM. Poor data management can lead to inaccurate reports, lost sales opportunities, and compliance issues. Security breaches can result in significant financial and reputational damage.
Best practices include:
- Data validation and cleansing: Implement data validation rules to ensure data accuracy and consistency. Regularly cleanse data to remove duplicates and outdated information. This ensures the data remains reliable and useful for decision-making.
- Access control and permissions: Implement strong access control measures to limit access to sensitive data. Assign roles and permissions based on job responsibilities. This protects sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Data backups and disaster recovery: Regularly back up your CRM data to prevent data loss in case of a system failure or disaster. Develop a comprehensive disaster recovery plan to ensure business continuity in the event of an unexpected outage.
- Security audits and compliance: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities. Ensure compliance with relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA.
CRM Integration with Other Business Tools
Integrating your CRM with other business tools can significantly enhance its functionality and value. Seamless integration streamlines workflows, improves data accuracy, and provides a more holistic view of your customer interactions.
Examples of integrations include:
- Email marketing platforms: Integrate your CRM with email marketing platforms like Mailchimp or Constant Contact to automate email campaigns and track email performance. This allows for personalized email communications and targeted marketing efforts.
- Marketing automation platforms: Integrate with marketing automation platforms like Marketo or HubSpot to automate marketing tasks, such as lead nurturing and campaign management. This frees up marketing teams to focus on strategic initiatives.
- Social media platforms: Integrate with social media platforms to monitor social media conversations and track customer interactions. This provides valuable insights into customer sentiment and allows for proactive customer service.
- Accounting software: Integrate with accounting software to automate invoicing and payment processing. This improves financial management and provides a more complete view of customer transactions.
Choosing the Right CRM Solution
Selecting the appropriate CRM system is crucial for maximizing its benefits. A poorly chosen system can lead to wasted resources and ultimately hinder sales and marketing efforts. Careful consideration of several key factors will ensure a successful implementation and long-term value.
CRM Pricing Models: Subscription versus One-Time Purchase
CRM systems are typically offered under two main pricing models: subscription-based and one-time purchase. Subscription models involve recurring monthly or annual fees, often tiered based on features and the number of users. This provides predictable budgeting and access to ongoing updates and support. One-time purchases, on the other hand, involve a single upfront payment for the software license. However, this often lacks ongoing support and may require separate payments for upgrades and maintenance. Choosing between these models depends largely on the company’s budget, long-term plans, and tolerance for risk. A smaller business with limited resources might favor a lower-cost subscription model, while a larger enterprise with more predictable finances might opt for a one-time purchase, acknowledging the need for future investment in upgrades.
CRM Selection Based on Business Size and Needs
The ideal CRM solution directly correlates with the size and specific needs of a business. Small businesses might find sufficient functionality in a simpler, less expensive CRM with basic contact management, sales tracking, and limited automation features. Larger enterprises, conversely, require more robust solutions capable of handling a greater volume of data, integrating with multiple systems, and supporting complex workflows and reporting. A critical consideration is the number of users, the required level of customization, and the integration capabilities needed to connect with existing systems like email marketing platforms and accounting software. For example, a small startup might benefit from a user-friendly cloud-based CRM like HubSpot Starter, while a multinational corporation might require a more comprehensive, on-premise solution like Salesforce Enterprise Edition tailored to its unique operational requirements.
Scalability and Future-Proofing a CRM
Choosing a scalable CRM is paramount for long-term success. The system should be capable of handling increased data volumes, user numbers, and evolving business needs without significant disruptions or expensive upgrades. This involves considering the CRM’s architecture, its ability to integrate with future technologies, and the vendor’s track record of providing timely updates and support. A cloud-based solution typically offers greater scalability compared to an on-premise system, as resources can be easily adjusted based on demand. Future-proofing also entails selecting a vendor with a proven history of innovation and a commitment to ongoing development, ensuring the CRM remains relevant and effective in the face of technological advancements. For example, a CRM that readily integrates with emerging AI-powered tools will be more future-proof than one that lacks such capabilities.
Checklist of Questions for Potential CRM Vendors
Before committing to a CRM provider, a thorough evaluation is essential. This involves compiling a comprehensive list of questions that directly address the business’s specific requirements and concerns. This checklist should encompass aspects like pricing, features, scalability, integration capabilities, support services, security measures, and the vendor’s reputation and track record. Examples of crucial questions include: What are the different pricing tiers and what features are included in each? What level of customization is possible? What integrations are available with other software systems? What is the vendor’s support policy and response time? What security measures are in place to protect data? What is the vendor’s experience with businesses of similar size and industry? Thorough answers to these questions will help businesses make an informed decision, ensuring they choose a CRM solution that perfectly aligns with their present and future needs.
Advanced Applications and Integrations
Modern CRM systems have evolved beyond basic contact management, leveraging advanced technologies and integrations to significantly enhance sales and marketing efforts. The integration of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and various business applications unlocks a wealth of capabilities, leading to improved efficiency, data-driven decision-making, and ultimately, increased revenue.
AI and Machine Learning in CRM
AI and machine learning are transforming CRM systems by automating tasks, predicting customer behavior, and personalizing interactions. AI-powered features such as predictive lead scoring can identify high-potential leads, allowing sales teams to prioritize their efforts. Machine learning algorithms analyze historical data to identify patterns and trends, enabling more accurate forecasting and resource allocation. For example, a CRM system could predict the likelihood of a customer churning based on their past interactions and engagement levels, allowing proactive intervention by customer support. This proactive approach helps retain valuable customers and reduce churn rates. Furthermore, AI-driven chatbots can handle routine customer inquiries, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex issues. These advancements significantly improve efficiency and customer satisfaction.
CRM Integration with Social Media Platforms for Lead Generation
Integrating CRM with social media platforms like LinkedIn, Twitter, and Facebook provides a powerful tool for lead generation. Social listening tools within the CRM can monitor brand mentions and conversations, identifying potential leads expressing interest in products or services. Social media posts and advertisements can be directly linked to CRM profiles, tracking campaign performance and attributing leads to specific sources. For instance, a LinkedIn ad campaign could be tracked within the CRM, showing which ads generated the most qualified leads. This allows for optimization of future campaigns based on data-driven insights. Furthermore, sales representatives can access social media profiles directly within the CRM, enabling personalized outreach and relationship building.
Benefits of Integrating CRM with Customer Support Systems
Integrating CRM with customer support systems, such as help desk software, provides a holistic view of the customer journey. This integration allows support agents to access complete customer history, including past interactions, purchase details, and support tickets, enabling them to provide more informed and personalized assistance. This improved service quality increases customer satisfaction and loyalty. For example, a support agent can quickly access a customer’s past purchase history to understand their needs and offer tailored solutions. Furthermore, the integration facilitates seamless escalation of issues, ensuring quicker resolution times and improved customer experience. This unified approach streamlines communication and improves efficiency across departments.
Examples of Successful CRM Integrations with Other Business Applications
Successful CRM implementations often involve integrating with other business applications to create a unified system. For example, integrating CRM with marketing automation platforms allows for automated email campaigns, lead nurturing sequences, and personalized messaging. Integrating with e-commerce platforms provides real-time sales data and customer purchase history. Integration with accounting software streamlines invoicing and financial reporting. A successful example could be a company using Salesforce CRM integrated with Marketo for marketing automation, Shopify for e-commerce, and NetSuite for accounting. This integrated system provides a single source of truth for all customer and business data, improving efficiency and decision-making across the organization.
Final Wrap-Up
Ultimately, the successful implementation of a CRM for Sales and Marketing Automation hinges on understanding its core capabilities and aligning its functionalities with your specific business objectives. By leveraging the insights provided here, businesses can harness the power of integrated systems to streamline workflows, enhance customer engagement, and drive significant growth. Remember, the right CRM isn’t just a tool; it’s a strategic investment in your future success.