Best Enterprise CRM Solutions: A Comprehensive Guide
Best Enterprise CRM Solutions are crucial for businesses aiming to streamline operations and enhance customer relationships. This guide delves into the essential aspects of selecting, implementing, and optimizing enterprise CRM systems, offering insights into vendor comparisons, key features, and crucial considerations for maximizing return on investment. We’ll explore the diverse needs of different enterprise departments and discuss strategies for successful implementation and ongoing management.
From defining your specific enterprise requirements and selecting the right vendor, to navigating the complexities of data migration and ensuring robust security, this guide provides a practical framework for businesses seeking to leverage the power of CRM to achieve their strategic goals. We’ll cover everything from cost analysis and ROI calculations to best practices for employee training and ongoing system optimization.
Defining Enterprise CRM Needs
Implementing a successful enterprise CRM system requires a clear understanding of the organization’s specific needs and objectives. A well-defined strategy ensures the chosen system aligns with business goals and delivers a measurable return on investment. This involves identifying core functionalities, establishing key performance indicators (KPIs), and understanding the varying requirements across different departments.
Core Functionalities of an Enterprise CRM System
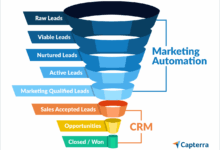
The core functionalities of an enterprise CRM system extend beyond basic contact management. A robust system integrates various business processes to provide a unified view of the customer journey. This integrated approach allows for streamlined operations and improved decision-making.
Essential CRM Functionalities
- Contact Management: Comprehensive storage and management of customer data, including contact information, interaction history, and purchase details. This ensures consistent and personalized interactions.
- Sales Force Automation (SFA): Tools for managing sales pipelines, tracking leads, automating sales processes, and improving sales forecasting accuracy. This leads to improved sales efficiency and increased revenue.
- Marketing Automation: Capabilities for managing marketing campaigns, tracking customer engagement, and personalizing marketing messages. This enables targeted marketing efforts and optimized campaign performance.
- Customer Service Management: Tools for managing customer inquiries, resolving issues, and tracking customer satisfaction. This enhances customer experience and builds loyalty.
- Reporting and Analytics: Dashboards and reports providing real-time insights into key business metrics, enabling data-driven decision-making and continuous improvement.
- Integration Capabilities: Seamless integration with other enterprise systems, such as ERP and marketing automation platforms, for a unified view of customer data. This minimizes data silos and improves operational efficiency.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Enterprise CRM Success
Measuring the success of an enterprise CRM system requires carefully selected KPIs aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives. These metrics provide insights into the effectiveness of the system and identify areas for improvement.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Measures the cost of acquiring a new customer. A lower CAC indicates greater efficiency in customer acquisition efforts.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): Predicts the total revenue generated by a customer over their relationship with the company. Higher CLTV signifies a more profitable customer base.
- Customer Churn Rate: Tracks the percentage of customers who stop doing business with the company. A lower churn rate reflects higher customer retention and loyalty.
- Sales Conversion Rate: Measures the percentage of leads that convert into paying customers. An increased conversion rate indicates improved sales effectiveness.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT): Measures customer satisfaction levels through surveys and feedback. High CSAT scores reflect positive customer experiences.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Measures the overall return on the investment made in the CRM system. A positive ROI demonstrates the system’s value to the organization.
Hypothetical Enterprise CRM Requirements: Global Retail Conglomerate
Imagine a large multinational retail conglomerate with diverse brands, operating across multiple countries and selling both online and in physical stores. Their CRM system needs to handle vast amounts of customer data, integrate with various e-commerce platforms and point-of-sale (POS) systems, and provide real-time insights into sales performance across different regions and product categories. The system must support multiple languages and currencies, comply with international data privacy regulations, and facilitate personalized marketing campaigns based on customer preferences and purchase history. Furthermore, robust customer service functionality is crucial to handle inquiries across various channels (phone, email, chat). The company would require sophisticated reporting and analytics capabilities to track key performance indicators across its diverse business units.
Comparative CRM Needs Across Departments
Different departments within an enterprise have distinct CRM requirements. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting and implementing a system that meets the needs of all stakeholders.
| Department | Specific CRM Needs |
|---|---|
| Sales | Lead management, opportunity tracking, sales forecasting, sales pipeline visualization, and sales performance reporting. |
| Marketing | Campaign management, lead nurturing, customer segmentation, marketing automation, and campaign performance analysis. |
| Customer Service | Case management, ticket tracking, knowledge base integration, customer interaction history, and customer satisfaction measurement. |
Top Enterprise CRM Vendors
Choosing the right Enterprise CRM solution is crucial for business success. The market offers a wide array of options, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Understanding the key players and their offerings is vital for making an informed decision. This section will analyze some of the leading vendors, comparing their features, pricing, and target markets.
Several vendors consistently rank among the top enterprise CRM solutions. Their market dominance stems from a combination of robust features, strong customer support, and extensive market penetration. Careful consideration of each vendor’s unique capabilities is necessary to align the solution with specific business needs.
Leading Enterprise CRM Vendors
The following table compares three major enterprise CRM vendors: Salesforce, Microsoft Dynamics 365, and SAP CRM. These platforms represent a range of approaches and cater to diverse organizational sizes and industry verticals. Note that pricing is highly variable and dependent on specific configurations and modules selected.
| Vendor | Features | Pricing Tiers | Target Customer Size | Unique Selling Proposition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salesforce | Sales Cloud, Service Cloud, Marketing Cloud, Commerce Cloud, extensive AppExchange ecosystem, robust customization options, AI-powered insights | Subscription-based, ranging from per-user monthly fees to enterprise-level contracts with significant volume discounts. Pricing varies greatly based on the number of users, features, and add-ons. | Small to very large enterprises; highly adaptable to various business sizes. | Extensive ecosystem of apps and integrations, highly customizable platform, market leader with a large user base and strong community support. |
| Microsoft Dynamics 365 | Integrated with the Microsoft 365 suite, strong business intelligence capabilities, robust project management tools, good for organizations already heavily invested in the Microsoft ecosystem. | Subscription-based, with various plans catering to different business needs and user counts. Pricing is often tiered based on functionality and user licenses. | Small to large enterprises; particularly strong within organizations already using Microsoft products. | Seamless integration with Microsoft’s other business applications, offering a unified and cohesive user experience. |
| SAP CRM (now part of SAP Customer Experience) | Strong integration with other SAP enterprise applications, comprehensive customer data management, robust analytics and reporting, often preferred in large, complex organizations. | Typically enterprise-level licensing agreements with pricing dependent on the number of users, modules, and implementation services. Pricing is often complex and negotiated individually. | Large enterprises; particularly suitable for organizations with complex business processes and existing SAP infrastructure. | Deep integration with SAP’s ERP and other enterprise systems, providing a holistic view of customer interactions within a larger business context. |
Key Features of Enterprise CRM Systems
A robust enterprise CRM system is far more than just a contact list; it’s a multifaceted platform designed to streamline operations, enhance customer relationships, and drive revenue growth. Its effectiveness hinges on a carefully selected suite of features working in concert to provide a holistic view of the customer journey and business processes. The key features described below represent the core functionalities that define a truly powerful enterprise CRM solution.
Contact Management
Effective contact management is the foundation of any successful CRM system. This involves more than just storing contact details; it includes the ability to segment contacts based on various criteria (demographics, purchase history, engagement levels), track interactions across multiple channels, and manage communication preferences. A well-implemented contact management system allows sales and marketing teams to personalize communications, leading to improved conversion rates and stronger customer relationships. For example, a CRM system might automatically segment customers who have made recent purchases into a “high-value” group, enabling targeted marketing campaigns offering exclusive discounts or early access to new products.
Sales Force Automation
Sales force automation (SFA) tools within a CRM system automate repetitive tasks, freeing up sales representatives to focus on higher-value activities like relationship building and closing deals. These tools typically include features such as lead management, opportunity tracking, sales forecasting, and pipeline management. By providing real-time visibility into the sales process, SFA helps sales teams prioritize leads, identify potential bottlenecks, and improve overall sales efficiency. A company using SFA might see a reduction in sales cycle length by 15% due to improved lead qualification and follow-up processes.
Marketing Automation
Marketing automation capabilities integrate seamlessly with contact management and SFA, enabling the creation and execution of targeted marketing campaigns. This includes features like email marketing, social media management, campaign tracking, and lead nurturing. By automating repetitive marketing tasks, businesses can improve efficiency and personalize customer interactions. For instance, automated email sequences can be triggered based on specific customer actions, such as website visits or form submissions, ensuring timely and relevant communication. A successful marketing automation strategy can significantly increase marketing ROI by automating processes and delivering personalized messages to the right customers at the right time.
Customer Service Capabilities
Excellent customer service is critical for building customer loyalty and advocacy. A CRM system enhances customer service by providing a centralized repository of customer information, allowing support agents to access a complete history of interactions and resolve issues efficiently. Features like case management, ticketing systems, and knowledge bases empower agents to provide faster and more effective support. Companies utilizing robust customer service features within their CRM often see improved customer satisfaction scores and reduced customer churn. For example, a self-service knowledge base can reduce the volume of support tickets by addressing common issues proactively.
Integration Capabilities
The true power of an enterprise CRM system lies in its ability to integrate with other critical business systems. Seamless integration with ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems provides a unified view of customer data, financial information, and inventory levels. Integration with marketing automation platforms ensures consistent messaging and data flow across sales and marketing efforts. These integrations eliminate data silos, improve data accuracy, and enable more informed decision-making. For example, integration with an ERP system allows sales representatives to access real-time inventory data, preventing overselling or promising delivery dates that cannot be met.
Advanced Analytics and Reporting
Enterprise CRM systems provide advanced analytics and reporting capabilities, allowing businesses to gain valuable insights into customer behavior, sales performance, and marketing effectiveness. These insights can be used to identify trends, optimize strategies, and improve overall business performance. Dashboards and custom reports provide a clear and concise overview of key metrics, facilitating data-driven decision-making. For example, sales managers can use CRM analytics to identify top-performing sales representatives, understand which marketing campaigns are most effective, and predict future sales trends.
Implementation and Deployment Strategies
Implementing an enterprise CRM system is a complex undertaking requiring careful planning and execution. Success hinges on choosing the right approach, managing data migration effectively, and providing comprehensive employee training. Different organizations will find different strategies most suitable, depending on their size, existing IT infrastructure, and business processes.
Phased Rollouts versus Big-Bang Implementations
Two primary approaches exist for deploying enterprise CRM systems: phased rollouts and big-bang implementations. A phased rollout involves implementing the CRM system gradually, typically department by department or business unit by business unit. This approach allows for iterative testing and refinement, minimizing disruption and allowing for adjustments based on feedback. A big-bang implementation, on the other hand, involves a simultaneous rollout across the entire organization. While faster, this approach carries a higher risk of disruption and requires more extensive upfront planning and preparation. The optimal approach depends on the organization’s risk tolerance and the complexity of its business processes. For example, a large multinational corporation with numerous interconnected departments might opt for a phased rollout to minimize operational disruption. A smaller company with simpler processes might find a big-bang implementation more efficient.
Data Migration from Legacy Systems
Migrating data from legacy systems to a new CRM platform presents significant challenges. Data inconsistencies, outdated formats, and the sheer volume of data can all complicate the process. Careful planning is crucial, including data cleansing, transformation, and validation to ensure data accuracy and integrity. This often involves employing specialized data migration tools and techniques to handle large datasets efficiently. Failure to properly migrate data can lead to inaccurate reporting, poor decision-making, and ultimately, the failure of the CRM implementation. For instance, a company migrating from a fragmented collection of spreadsheets and databases to a unified CRM system might encounter inconsistencies in customer data (e.g., multiple entries for the same customer with conflicting information), requiring significant data cleansing before migration.
Step-by-Step Implementation Plan
A successful enterprise CRM implementation requires a well-defined plan. This plan should include the following steps:
- Needs Assessment and Requirements Gathering: Define specific business needs and objectives for the CRM system. This involves identifying key stakeholders and gathering their input.
- Vendor Selection and System Configuration: Choose a CRM vendor and configure the system to meet the organization’s specific needs. This includes customizing workflows, dashboards, and reports.
- Data Migration: Plan and execute the migration of data from legacy systems. This involves data cleansing, transformation, and validation.
- System Testing: Thoroughly test the system to identify and resolve any bugs or issues before the full rollout.
- User Training: Provide comprehensive training to employees on how to use the new system effectively. This might involve classroom training, online tutorials, or on-the-job coaching.
- Go-Live and Post-Implementation Support: Launch the system and provide ongoing support to users to address any issues or questions.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Optimization: Continuously monitor system performance and make adjustments as needed to ensure optimal efficiency and effectiveness.
Employee Training Best Practices
Effective employee training is crucial for the success of any CRM implementation. A multi-faceted approach is recommended, incorporating various training methods to cater to different learning styles. This might include:
- Instructor-led training: Provides hands-on experience and allows for immediate feedback.
- Online tutorials and e-learning modules: Offers flexibility and allows employees to learn at their own pace.
- On-the-job coaching and mentoring: Provides personalized support and guidance.
- Gamification: Makes training more engaging and fun, improving knowledge retention.
- Regular refresher courses: Ensures that employees stay up-to-date with the latest system features and updates.
Providing ongoing support and readily available resources, such as FAQs, help desk support, and user manuals, are essential to ensure user adoption and continued system usage. Failure to adequately train employees can lead to low adoption rates, poor data quality, and ultimately, the failure of the CRM implementation.
Cost and Return on Investment (ROI)
Implementing an enterprise CRM system represents a significant investment. Understanding the associated costs and potential return is crucial for justifying the expenditure and ensuring successful deployment. This section details the various cost components, methods for measuring ROI, strategies for cost optimization, and a hypothetical cost-benefit analysis for a mid-sized enterprise.
Cost Components of Enterprise CRM Systems
The total cost of ownership (TCO) for an enterprise CRM system extends beyond the initial software license fees. Several factors contribute to the overall expense, and accurate budgeting requires consideration of each.
- Software Licenses: This is the upfront cost for purchasing the CRM software itself. Pricing models vary depending on the vendor, the number of users, and the features included. Expect variations based on cloud-based vs. on-premise solutions, with cloud-based often presenting a subscription model.
- Implementation Costs: These costs cover the services required to set up and configure the CRM system, including data migration, customization, and integration with existing systems. Consultancy fees and project management are significant components.
- Training Costs: Effective CRM adoption relies heavily on user training. This encompasses initial training sessions for all users, ongoing support, and potentially specialized training for administrators.
- Ongoing Support and Maintenance: This includes technical support, software updates, and bug fixes. Many vendors offer different support tiers with varying levels of service and cost.
- Hardware and Infrastructure Costs (On-Premise): For on-premise deployments, significant investment in servers, network infrastructure, and IT personnel is necessary. Cloud-based solutions significantly reduce these costs.
Measuring the ROI of CRM Investment
Organizations can measure the ROI of their CRM investment through various metrics, focusing on both quantifiable and qualitative improvements.
- Increased Sales Revenue: Tracking sales growth directly attributable to improved lead management, sales forecasting, and customer relationship management capabilities provides a strong indicator of ROI.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Measuring customer satisfaction through surveys and feedback mechanisms demonstrates the impact of improved service and communication. Higher satisfaction often translates to increased loyalty and repeat business.
- Reduced Customer Churn: Lower customer churn rates indicate improved customer retention, leading to increased lifetime value and a positive return on investment.
- Increased Sales Efficiency: Measuring metrics like sales cycle length, conversion rates, and average deal size can highlight improvements in sales team productivity.
- Improved Marketing ROI: Tracking marketing campaign effectiveness and attributing leads and sales to specific campaigns helps demonstrate the return on marketing investments integrated with the CRM.
Strategies for Optimizing CRM Cost-Effectiveness
Several strategies can help organizations maximize the value derived from their CRM investment while minimizing costs.
- Careful Vendor Selection: Thoroughly evaluating vendors and selecting a solution that aligns with specific business needs and budget constraints is critical.
- Phased Implementation: Implementing the CRM system in phases, starting with core functionalities and gradually adding more features, can help control costs and manage risks.
- Effective User Adoption: Investing in comprehensive training and providing ongoing support ensures that users effectively utilize the system, maximizing its benefits.
- Regular System Optimization: Regularly reviewing and optimizing CRM processes and configurations can improve efficiency and reduce unnecessary expenses.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: Cloud-based CRM solutions often offer lower upfront costs and reduced ongoing maintenance expenses compared to on-premise deployments.
Hypothetical Cost-Benefit Analysis for a Mid-Sized Enterprise
Let’s consider a mid-sized enterprise with 100 employees, currently experiencing a 15% customer churn rate and an average deal size of $10,000. They are considering a cloud-based CRM solution with an annual license fee of $10,000, implementation costs of $20,000, and annual training and support costs of $5,000.
Assume that the CRM system reduces customer churn by 5% and increases the average deal size by 10%. This translates to:
Reduced churn: (0.15 – 0.10) * (annual sales volume) = 0.05 * (annual sales volume)
Increased deal size: 0.10 * (annual sales volume) = 0.10 * (annual sales volume)
Assuming an annual sales volume of $1,000,000 before CRM implementation:
Annual savings from reduced churn: 0.05 * $1,000,000 = $50,000
Increased revenue from larger deals: 0.10 * $1,000,000 = $100,000
Total annual benefit: $50,000 + $100,000 = $150,000
Total annual cost: $10,000 (license) + $5,000 (support) = $15,000 (excluding initial implementation cost)
Net annual benefit (excluding implementation): $150,000 – $15,000 = $135,000
The initial investment of $20,000 is recouped within a short period, demonstrating a strong positive ROI. This is a simplified example, and a more detailed analysis would consider other factors, but it illustrates the potential benefits of a well-chosen and implemented CRM system.
Security and Data Privacy Considerations
Enterprise CRM systems, while offering significant business advantages, present substantial security and data privacy challenges. The sensitive nature of customer data stored within these systems necessitates a robust security posture and strict adherence to relevant regulations. Failure to adequately address these concerns can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions.
Key Security Risks and Mitigation Strategies
Several key security risks are inherent to enterprise CRM systems. These include unauthorized access, data breaches, malware infections, and insider threats. Effective mitigation strategies involve a multi-layered approach encompassing technical, administrative, and physical security measures. This includes implementing strong access controls, such as multi-factor authentication and role-based access permissions, to limit access to sensitive data based on individual user needs. Regular security audits and penetration testing help identify vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Furthermore, robust data encryption, both in transit and at rest, protects data from unauthorized access even if a breach occurs. Employee training programs focused on security awareness and best practices help minimize the risk of insider threats. Finally, employing a comprehensive security information and event management (SIEM) system allows for real-time monitoring of the CRM system for suspicious activities and rapid response to security incidents.
Data Privacy and Compliance with Regulations
The importance of data privacy cannot be overstated. Regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States impose stringent requirements on how organizations collect, process, and protect personal data. Compliance necessitates implementing data minimization practices, obtaining explicit consent for data processing, and providing individuals with control over their data, including the right to access, rectification, and erasure. Organizations must also establish clear data governance policies and procedures, including data retention policies that comply with legal requirements. Regular privacy impact assessments help identify and mitigate potential privacy risks. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in substantial fines and legal action.
Ensuring the Security and Integrity of Customer Data
Maintaining the security and integrity of customer data within a CRM system requires a proactive and comprehensive approach. This involves implementing robust access controls, data encryption, and regular security updates to the CRM software and underlying infrastructure. Data loss prevention (DLP) tools can help prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s network unauthorized. Regular data backups are crucial to ensure business continuity in case of data loss or system failure. Data masking and anonymization techniques can be employed for testing and development purposes to protect sensitive data. Furthermore, establishing a clear incident response plan outlines procedures to follow in the event of a security breach, minimizing the impact on customers and the organization.
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery Planning
Comprehensive data backup and disaster recovery planning are critical for ensuring business continuity and minimizing the impact of unforeseen events. Organizations should implement a robust backup strategy that includes regular backups of the CRM database, configuration files, and other critical data. Backups should be stored securely offsite, ideally in a geographically separate location, to protect against physical damage or disaster at the primary location. A disaster recovery plan should detail procedures for restoring the CRM system and data in the event of a failure, including testing and validation of the recovery process. This plan should also include strategies for communicating with customers and stakeholders during a disruption. The frequency of backups and the retention period should be determined based on the organization’s risk tolerance and recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs). For example, a financial institution might require more frequent backups and shorter RPOs than a smaller retail business.
Last Point
Ultimately, the selection and implementation of an enterprise CRM system is a strategic decision demanding careful consideration of various factors. By understanding the core functionalities, vendor landscape, implementation strategies, and security considerations outlined in this guide, businesses can make informed choices to optimize their CRM investment and foster stronger customer relationships. The key is a holistic approach that aligns technology with business objectives, ensuring a seamless integration and maximizing the potential for growth and improved efficiency.